Marine Corps Body Composition Study leads to Modernization of Policies
The military is well known for its physical fitness and body composition standards – standards that were set more than 40 years ago when President Jimmy Carter directed a review of physical fitness for military services. These standards were developed intending to promote the physical readiness of military troops and to prevent obesity.
While the Marine Corps is no stranger to modernizing human performance policies and standards, this is the most comprehensive assessment of body composition methods since President Carter directed the review in 1980. In 2017, the Marines further emphasized performance by incentivizing high fitness test scores with either an increase in total allowable body fat or an exemption from body composition testing for top tier performers.
And now, the Marines collaborated with scientists from the U.S. Army Research Institute of Environmental Medicine to conduct a multi-center study assessing the USMC Body Composition and Military Appearance Program.
The research and analysis provided by USARIEM provided valuable insights to the service and informed the most significant modernization of human performance standards in the service's recent history.
"This comprehensive study obtained data from 2,175 Marines," explains Dr. Adam Potter, research physiologist and mathematical physiologist for USARIEM and lead principal investigator for this project. "Women comprised one third of this total for adequate sampling to evaluate the performance of the current methods and standards for women and men."
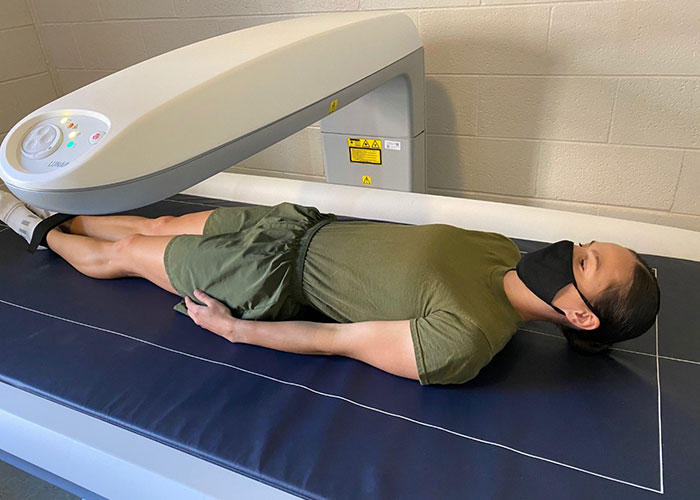
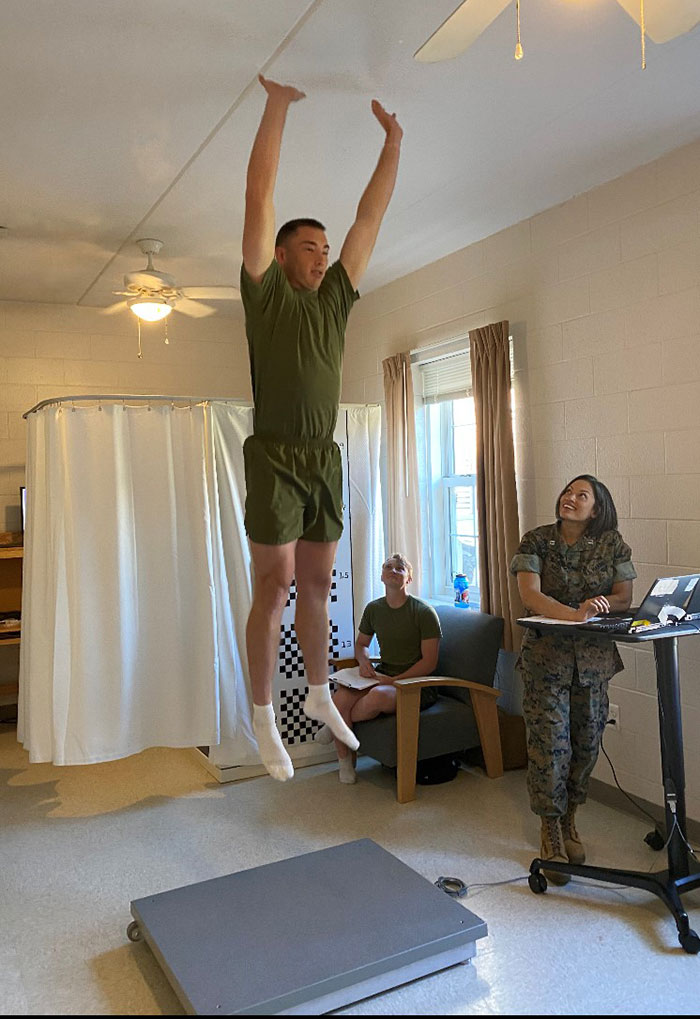
Marines volunteering for this study came from four locations: The Basic School, Marine Corps Base Quantico, Virginia; the National Capital Region in-and-around Quantico, Virginia; Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune, North Carolina; and Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton, California. At these locations, volunteers took part in a series of testing, including body dimensions, the "tape test," and research-grade evaluation of body composition using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), whole body three-dimensional scans, and strength testing based on jump performance on calibrated force platforms. Researchers collected participants' demographic information, self-reported health and fitness behaviors, and most recent official physical and combat fitness test results.

"The report revealed that Marines are a lean force, with an average percent body fat of 22% for men and 30% for women," said Potter. "This was well below national civilian averages, matched by sex and age and measured by DXA as the gold standard method of body composition determination."
Results highlighted the current interrelationship between weight screening and body fat testing.
- Female Marines who failed the weight screen usually failed percent body fat standards as well, while 30% of men who failed weight met body fat standards.
- Most significantly, without the weight screen, an additional 9% of all men and 30% of all women would fail body fat standards.
Tape-test performance was compared to the DXA gold standard method, revealing the accuracy, overestimation, and underestimation of the tape.
- Accurately categorized 91.5% of men and 92.1% of women for their body fat standards.
- Overestimated 0.6% of men and 6.3% of women.
- Underestimated 7.9% of men and 1.6% of women.
Based on an analysis of the data, a small percentage of mis-categorized men and women would benefit from a body fat assessment by a more sophisticated method, such as DXA. The report also showed that body size, or the body mass index, had poor correlations with physical performance testing.

The study findings were briefed to Marine Corps leadership and ultimately, to General David Berger, Commandant of the Marine Corps, leading to the following formalized modifications to Marine Corps policy:
- Effective January 1, 2023, the Marine Corps will be the first service to validate the tape-test by qualified BIA or DXA for all Marines. To enable this self-imposed requirement, the Training and Education Command is in the process of fielding an initial 257 BIAs to units worldwide.
- Effective January 1, 2023, the Marine Corps will increase the total allowable female body fat standards by 1% for all women in order to more closely align male and female standards when accounting for biological differences.
- The Marine Corps will retain the 1% body fat allowance as a performance exemption for a composite score of 250 or above on both the physical and combat fitness test.
- The Marine Corps will retain the performance exemption from all body composition standards for a composite score of 285 or above on both the physical and combat fitness test.
"Any future recommendations to further modify service-level assessment methods would require additional research," said Potter.
Several peer-reviewed scientific articles have already been published, with publication of more analyses planned. The Army and the Navy have recently started their own body composition standards studies to address questions specific to service readiness requirements.
The technical report, "US Marine Corps Body Composition and Military Appearance Program (BCMAP)" Study, released in October, is publicly available here
USARIEM is a subordinate command of the U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command under the Army Futures Command. USARIEM is internationally recognized as the DOD's premier laboratory for Warfighter health and performance research and focuses on environmental medicine, physiology, physical and cognitive performance, and nutrition research. Located at the Natick Soldier Systems Center in Natick, Massachusetts, USARIEM's mission is to optimize Warfighter health and performance through medical research.













